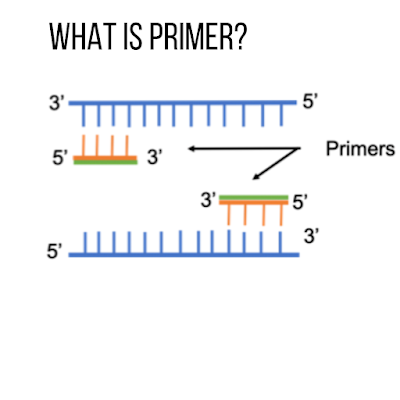
Primers are short single-stranded DNA or RNA molecules that serve as starting points for DNA synthesis. They are essential components of various molecular biology techniques, such as PCR (polymerase chain reaction), DNA sequencing, and site-directed mutagenesis.
In this post, we will explore the function of primers, their
design, and their importance in molecular biology. We'll also highlight why
they are critical for successful PCR amplification.
Function of Primers in
Molecular Biology
Primers are designed to provide a complementary starting
point for DNA polymerase, which is responsible for synthesizing new DNA
strands. During PCR, primers anneal to the template DNA at specific sites, and
then DNA polymerase extends the primers by adding nucleotides in the 5' to 3'
direction. This process creates complementary DNA strands that are synthesized
from the primers, and the cycle is repeated to generate multiple copies of the
DNA fragment of interest.
Design of Primers in
Molecular Biology:
The design of primers is crucial to the success of PCR and
other molecular biology techniques. Primers must be specific to the target DNA
sequence to ensure that only the desired fragment is amplified. Specificity is
achieved by designing primers to anneal to a unique sequence on the template
DNA, typically regions that are highly conserved or unique mutations in the DNA
sequence.
In addition to specificity, primers should have a melting
temperature that allows for efficient annealing to the template DNA. The
optimal melting temperature for a primer is typically between 50-65°C.
Finally, primers should not form hairpin loops or other
secondary structures that could interfere with annealing or extension by the
DNA polymerase. Secondary structures occur when complementary base pairs within
a single strand of DNA or RNA bind to each other, causing the strand to fold
back on itself. This can cause the primer to anneal to itself rather than the
template DNA, resulting in failed PCR amplification.
Importance of Primers
in Molecular Biology:
Primers are essential for many molecular biology techniques,
particularly PCR. PCR is a powerful tool for amplifying specific regions of DNA
and has many applications, including DNA sequencing, cloning, and diagnostic
testing. However, PCR amplification is only successful when the primers are
specific to the target DNA sequence and are designed correctly.
In conclusion, primers are critical components of many
molecular biology techniques, and their specificity, melting temperature, and
potential secondary structures must be carefully considered to ensure the
success of the experiment. They are essential for successful PCR amplification,
and their importance cannot be overstated.




0 Comments